
1. Sore Muscles:
The most common effect of poor posture are sore muscles. As you slouch, the muscles have to work harder to keep the spine stabilized and protected. The extra work on these muscles can cause muscle tightness, pain, and fatigue. This can lead to chronic issues with tight, painful and sore muscles from the neck all the way down to the lower back. Two major muscle groups that bare the brunt of these issues are the flexors and extensors of the trunk, which allow you to bend forward and lift objects. Overworking these muscles aren't good while they can also lead to spinal curvature due to the pressure.
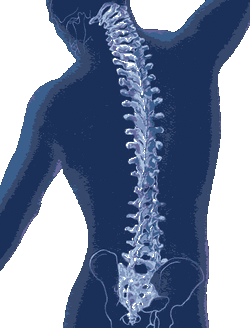
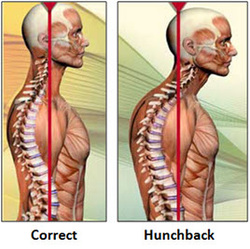
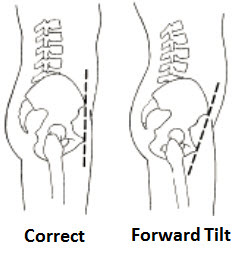
2. Spinal Curvature:
This is one of the most serious issues that can occur with bad posture, developing a spinal curvature. According to the Chiropractic Resource Organization, the human spine has four natural curves that make up an "s" shape (Picture and definition in "What is an Actual Good Posture" on the categories bar to the right). When bad posture is practiced, the spine may experience pressure, which slowly influences the spine curves and changes their positions. The spine is specifically designed to help absorb shock and keep you balanced, but as the spinal position changes, this ability becomes compromised. If you start having a habit of being in bad postures for a long time, when you grow old, you may develop permanent spinal curvatures (leading to subluxations), making it hard for you to bend.
3. Subluxations:
Once the spinal chord is curved and altered, one major issue that can occur are subluxations. Vertebral subluxations occur when a vertebrae become misaligned from the rest of the spine. This affects the overall integrity of the rest of the spinal column. These misalignments can eventually cause chronic health problems including stress and irritation of surrounding spinal nerves.
4. Blood Vessel Constriction:
As bad posture changes the alignment of the spine, the resulting changes and subluxations may cause problems regarding blood vessel constrictions. The constriction of the blood vessels around the spine can cut off blood supply to the cells of the muscles, which can affect nutrient and oxygen supply. Blood vessel constriction can also raise your chances of clot formation and issues with deep vein thrombosis.
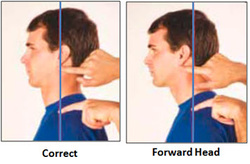
5. Nerve Constriction:
One of the most common side effects of a bad posture is nerve constriction. As the spine curves in shape, the resulting changes or subluxations can put pressure on the surrounding spinal nerves. Since the nerves that connect to the spine come from all over the body, these pinched nerves can not only cause neck and back pain but may also cause pain in other unrelated areas of the body.
6. Deepens depression:
Bad postures not only has effects in the physical health you are in. In a recent study from San Francisco State University, an experiment asked the students to either walk down a hall in a slouched position or to skip. The slouchers reported increased feelings of depression and lower energy than skippers. This psychological behavior is another reason for you to avoid being in bad postures.
7. Social Problems:
Bad postures also affect the way other people view you. Being in a bad posture doesn’t just hurt your attitude—it can affect how people see you. “You don’t want to walk into somebody’s office slouching and bent over, because people really do perceive you as not as vital,” says Janice Novak, author of Posture, Get it Straight. Your postures is a sign of your status sometime, with a great posture, you give out the signs that you are a confident successful person while vise versa, having a bad, slouched posture can give signs that you are a lazy or unconfident person.
Sources:
http://whatsyourposture.com.au/posture-health/
http://www.prevention.com/health/healthy-living/how-bad-posture-affects-your-health-and-happiness/2-causes-career-problems
http://www.livestrong.com/article/31223-negative-effects-poor-posture/
The most common effect of poor posture are sore muscles. As you slouch, the muscles have to work harder to keep the spine stabilized and protected. The extra work on these muscles can cause muscle tightness, pain, and fatigue. This can lead to chronic issues with tight, painful and sore muscles from the neck all the way down to the lower back. Two major muscle groups that bare the brunt of these issues are the flexors and extensors of the trunk, which allow you to bend forward and lift objects. Overworking these muscles aren't good while they can also lead to spinal curvature due to the pressure.
2. Spinal Curvature:
This is one of the most serious issues that can occur with bad posture, developing a spinal curvature. According to the Chiropractic Resource Organization, the human spine has four natural curves that make up an "s" shape (Picture and definition in "What is an Actual Good Posture" on the categories bar to the right). When bad posture is practiced, the spine may experience pressure, which slowly influences the spine curves and changes their positions. The spine is specifically designed to help absorb shock and keep you balanced, but as the spinal position changes, this ability becomes compromised. If you start having a habit of being in bad postures for a long time, when you grow old, you may develop permanent spinal curvatures (leading to subluxations), making it hard for you to bend.
3. Subluxations:
Once the spinal chord is curved and altered, one major issue that can occur are subluxations. Vertebral subluxations occur when a vertebrae become misaligned from the rest of the spine. This affects the overall integrity of the rest of the spinal column. These misalignments can eventually cause chronic health problems including stress and irritation of surrounding spinal nerves.
4. Blood Vessel Constriction:
As bad posture changes the alignment of the spine, the resulting changes and subluxations may cause problems regarding blood vessel constrictions. The constriction of the blood vessels around the spine can cut off blood supply to the cells of the muscles, which can affect nutrient and oxygen supply. Blood vessel constriction can also raise your chances of clot formation and issues with deep vein thrombosis.
5. Nerve Constriction:
One of the most common side effects of a bad posture is nerve constriction. As the spine curves in shape, the resulting changes or subluxations can put pressure on the surrounding spinal nerves. Since the nerves that connect to the spine come from all over the body, these pinched nerves can not only cause neck and back pain but may also cause pain in other unrelated areas of the body.
6. Deepens depression:
Bad postures not only has effects in the physical health you are in. In a recent study from San Francisco State University, an experiment asked the students to either walk down a hall in a slouched position or to skip. The slouchers reported increased feelings of depression and lower energy than skippers. This psychological behavior is another reason for you to avoid being in bad postures.
7. Social Problems:
Bad postures also affect the way other people view you. Being in a bad posture doesn’t just hurt your attitude—it can affect how people see you. “You don’t want to walk into somebody’s office slouching and bent over, because people really do perceive you as not as vital,” says Janice Novak, author of Posture, Get it Straight. Your postures is a sign of your status sometime, with a great posture, you give out the signs that you are a confident successful person while vise versa, having a bad, slouched posture can give signs that you are a lazy or unconfident person.
Sources:
http://whatsyourposture.com.au/posture-health/
http://www.prevention.com/health/healthy-living/how-bad-posture-affects-your-health-and-happiness/2-causes-career-problems
http://www.livestrong.com/article/31223-negative-effects-poor-posture/








 RSS Feed
RSS Feed